Bacterial, Viral Infection And Its Types

Preventing From Viral Infections During Pregnancy
January 16, 2020
Building Your Immunity During A Pandemic
January 20, 2020Bacteria are primitive organisms that have been existing along with humans since the beginning of time. They are often more useful to us than not. Very few have proven otherwise and have caused diseases in us. Several studies are going on about the different viral infections and its types. This could help you in recognizing the pattern in symptoms and get diagnosed for early treatment and recovery. Bacteria assist our body in gaining immunity, improving digestion and assimilation of vitamins. Owing to their microscopic single-celled nature, their presence in this world goes undetected to the common man. The air that we breathe, the food that we eat, the chair that we sit on, and even the clothes that we wear are home to millions of bacteria that may or may not help us positively.
Understanding Different Causes Of Infections
Since bacteria are present inside our body, it could affect any part anytime. Infection is when a harmful set of these microorganisms multiply in large numbers and spread throughout the strata. Food poisoning, Pneumonia, Meningitis are a few examples of viral infection and its types depend on the bacteria responsible for the attack. Food poisoning is when a bacterial infection is in the digestional tract. When the infection affects the lungs, it causes Pneumonia. When bacteria affect the layer around the brain and central nervous system, it causes Meningitis. There are three types of bacteria classified based on their shapes as spherical, helical and rod-shaped. The spherical-shaped bacteria are known as cocci, spirilla are helical-shaped, and bacilli are the Rod-shaped ones. Depending on their thick cell wall, they are further classified as gram-positive and gram-negative. Gram-positive is when they have a thick cell wall while gram-negative is when they do not have one. Tests such as antibiotic sensitivity determination with bacterial culture, gram staining all help identify the bacterial infection, and a medical practitioner could suggest treatment accordingly.
Read More About : All You Need To Know About Coronavirus And COVID-19
The virus is smaller microorganisms than bacteria. They are known to be disease-causing almost at all times known for their presence detection. Bacteria can reproduce on their own irrespective of the environment in which they thrive. Virus, on the other hand, only replicates in a host body by affecting the host DNA. Symptoms of bacterial infections and viral infections are often similar and hard to differentiate. A few symptoms such as cough, runny nose, fatigue and headache exist for bacterial infections such as sinus infections as well as viral infections such as a common cold. Length of illness, other additional symptoms as well as fluid tests in the lab are necessary for a medical practitioner to come to a conclusive diagnosis.
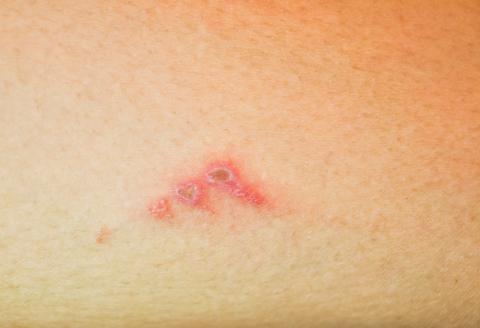
Different Bacterial Infections Through Skin And Food
Gram-positive bacteria often cause skin viral infection and its types derive from Streptococcus or Staphylococcus. These are usually on the outer surface of the skin and cause painful reactions. Cellulitis is one such infection which causes reddening of the skin. The infected area gets warm on touch. Although it occurs on legs, there is a high chance for it to spread to almost any part of the body. Bacteria cause deeper skin infections as well, such as boils. They are hair follicles that are covered by dust or dirt and lead to pus-filled bumps. Another hair follicle infection is folliculitis. These are swollen red bumps, similar to pimples, and occur due to bacteria from pools. Fluid-filled sores that occur on the skin and may lead to blisters or crusts are a symptom to another bacterial infection called impetigo. Depending on the causative bacteria, medical practitioners advice topical ointments or oral medication to treat bacterial skin infections.
Food poisoning is the digestive system under attack, and often bacteria are the black sheep. Symptoms are headache, nausea, fever, vomiting, chills, abdominal pain and diarrhoea. Improper food handling and preparation are the culprits. Most bacteria become inactive beyond a specific temperature, and when food is not cooked correctly, it often leaves the bacteria active. Dairy products, raw meat, eggs, fish are few of the items that need to be consumed earliest after procurement. Escherichia coli is the bacteria responsible for most food poisoning cases. The symptoms are bloody diarrhoea accompanied by fever, fatigue, nausea, headache, abdominal cramps and vomiting. The bacteria salmonella causes diarrhoea, fever and abdominal cramps that go away within the week.
Treatment And Recovery
Antibiotic is the one-word solution to viral infection and its types determine the treatment procedure accordingly. This medicine works to prevent the rapid growth of bacteria by reacting according to the cell structure of the bacteria. This is why antibiotics need to be consumed as per the prescription and directions given by your physician. A failure to comply may be more harmful to your body. Viral infections may not be brought down by antibiotics as they are designed for bacteria and not viruses. Consumption of prescribed antibiotics is advised by the physician to prevent any secondary infections due to bacteria. In the onset of one disease, there is often a chance for another one due to decreased immunity, and this is called a secondary infection.
Continued and overuse of antibiotics leads to the situation in which the good bacteria in our body get removed while the body becomes resistant to antibiotics. This is severe as it leaves the body open to attack from foreign bodies that might even lead to death. Due to the overuse, bacteria are no longer sensitive to the medicine that eliminates an infection. Around 10% of all the bacterial infections are due to antibiotic resistance, and nearly 1% are fatal. The bacteria responsible for infection after antibiotic resistance is Clostridium difficile. These thrive in a scenario where the antibiotic resistance is high. Deaths due to this are often recorded among patients under treatment or using prescription drugs. Hence it is very crucial to keep in check the infections in our bodies with regular check-ups and lab tests.