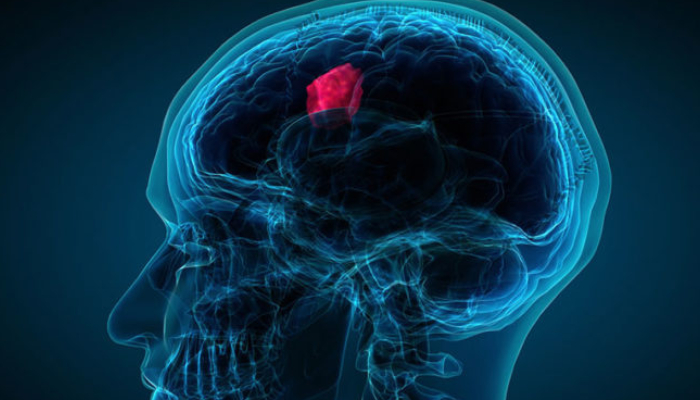
Diagnosis And Treatment For Brain Tumours

Causes, Diagnosis And Medical Treatments For Autism
March 16, 2020
Diagnosis And Medical Treatments For Asthma
March 20, 2020What Is A Brain Tumour?
Mass of tissue that is formed by accumulation of malignant or abnormal cells. It is normal that cells in the bodies are replaced as they age and die. This cycle can be disrupted by diseases like cancer that affects the growth of cells. Tumour cells don’t die like the normal cells and they also grow as more and more cells get added to the mass. A brain tumour is the one that originates in the brain. There are more than a lakh new cases of brain tumour diagnosed every year. It is most commonly found in people aged between 65 and 79. Children who have received radiation are at higher risk of having brain tumours as they age.
Primary brain tumours are benign, which is, they are not cancerous or aggressive. They do not spread to other tissues. Benign tumours can be serious and at times life threatening. The primary brain tumours emerge from cells in the brain and the central nervous systems. The most common type of tumours that affect adults are gliomas and meningeal tumours. Astrocytic brain tumours or gliomas form from glial cells or astrocytes that keep nerves healthy. Meningeal tumours form in the meninges which is a thin layer of tissue between brain and spinal cord. A malignant brain tumour originates in the brain and spreads to other organs including the central nervous system.
Read More About : All You Need To Know About Psychotic Disorders
Symptoms Of Brain Tumour
Diagnosis and treatment for brain tumours depend on the symptoms. The symptoms of brain tumour vary based on the type of the brain tumour and its location. Brain controls different areas and functions of the body. So the location of the tumour is vital as it might hamper the function of the body activated by the brain cells of the tumour. In a few cases, there are no symptoms unless the tumour has grown quite big and in a few cases the symptoms slowly spread and affect the body. Rapid decline in health and serious health conditions are some of the main symptoms.
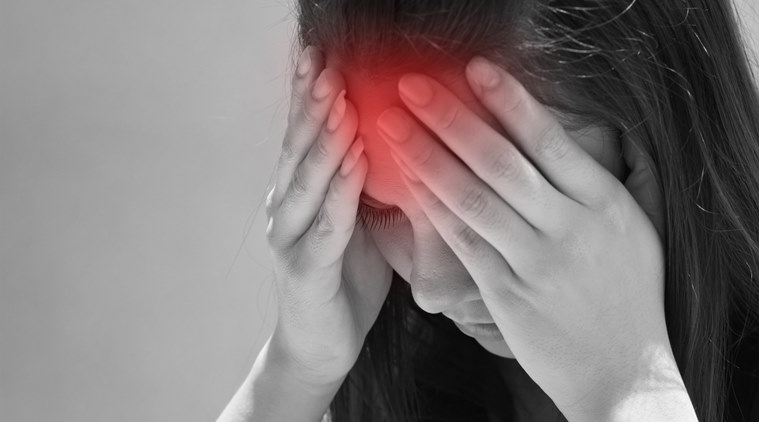

Initially, it may start with mild headaches that slowly will turn aggressive. Not all headaches are related to brain tumours. But if the headache is persistent then you might as well get it checked. Numbness and tingling in the arm and legs with problems in walking and balancing is one kind of symptom. At times, one may get seizure and loss of memory. Personality changes with difficulty to concentrate, changes in vision, speech and hearing, and vomiting due to nausea in the morning.
Diagnosis And Treatment
Healthcare providers will first conduct a physical examination of the symptom and based on the findings will request for tests. They will require detailed images of the brain that can be done through MRI or CT Scan. MRA or Angiogram involves using x-rays and dye to get a deeper look into the brain cells and blood vessels for abnormality and signs of tumour. A biopsy will determine if the tumour is cancer. Biopsy requires tissue samples from the brain that can be removed from the tumour through surgery or by drilling a hole into the skull.
The first and foremost thing done in the initial stages of the treatment is the removal of tumour through surgery. Surgery may not be possible due to the location of the tumour in some cases for which radiation or chemotherapy is recommended. This will shrink the tumour and at time will kill the cancerous cells. There could be possible side effects and other long term effects during the course of this treatment. It is important that you discuss this with the doctors and plan for rehabilitation after the treatment. There are different therapies like physical therapy, speech therapy and occupational therapy to help manage daily activities.