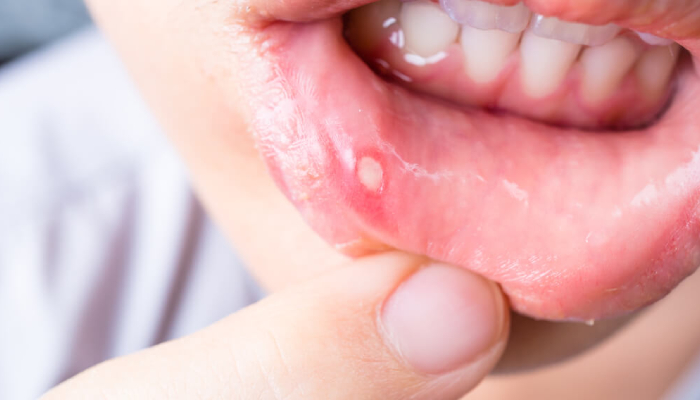
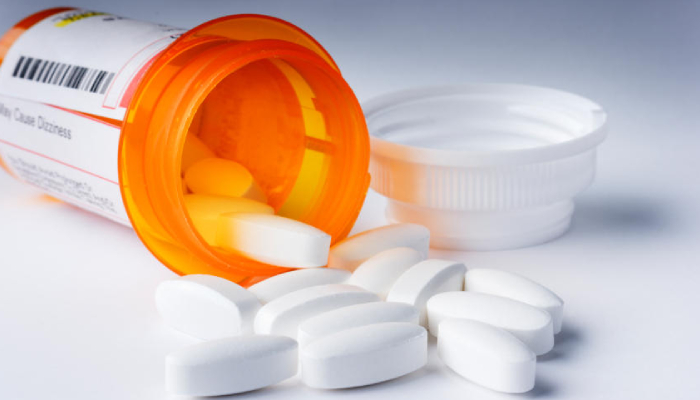
How Harmful Can Mouth Sores Be?

Keeping Your Immune System Healthy With Supplements
January 22, 2020
Things To Know About Antibiotics and Viral Infections
January 26, 2020Mouth Sores: What are they?
A mouth sore is as common as a headache. Found anywhere inside the oral cavity, these sores are distinctive in their pain and appearance. Mouth sores can even develop in the oesophagus.
When it comes to mouth sores, there’s good and bad news. The good news is that, in spite of being quite painful, these sores will mostly heal on their own. The bad news is that some of these sores can be an indication of an underlying problem like oral cancer or a viral infection.
Let’s delve into an in-depth discussion about all there is to know with mouth sores.
Read More About : Keeping Your Immune System Healthy With Supplements
Know the different types of mouth sores
They might all look similar but each mouth sore is distinct right from the appearance to the reasons that cause them. Here’s a crystal clear compilation of the types of mouth sores:
| Type of mouth sore | Appearance and symptom | Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Canker Sores or mouth ulcers or aphthous ulcers | Painful oval shaped ulcers in red, yellow or white colour. Occur on the gums or lining of the cheeks. | Celiac disease, deficiency of vitamins, Crohn’s disease or HIV. |
| Cold sores | Painful blisters on the lips.Accompanied by symptoms like mild fever, swollen lymph nodes and body pain. | Herpes simplex type 1 virus (HSV1) or Herpes Simplex type 2 virus (HSV2) |
| Gingivostomatitis | Commonly found in children. Symptoms include sore throat, fever and swollen lymph nodes. | Viral or bacterial infection. Poor oral hygiene |
| Oral thrush | Characterised by white, creamy bumps that appear on the tongue, inner cheeks, gums and tonsils. Symptoms include pain, loss of taste and difficulty in swallowing. | Yeast infection, weakened immune system due to chronic illnesses like cancer or HIV. |
| Folate deficiency | Swelling of the tongue or sores in the delicate lining of the mouth. | Anemia and deficiency of folate, a water-soluble vitamin. |
| Oral lichen planus | Characterised by white, lacy patches on the tongue that resemble spider webs. Patches can also be tender and swollen and may occur in the gums, cheeks and tissues of the lips. | Auto-immune disorders Oral infections Prolonged intake of medication Allergies caused by food or dental appliances |
| Leukoplakia | Thick, white raised patches on the tongue. Leukoplakia can also be a symptom of oral cancer. | Excessive smoking and alcohol intake. |
| Oral cancer or mouth cancer | Ulcers, white or red patches that do not heal. Oral cancer can manifest itself in the gums, cheeks, lips, tongue and roof and floor of the mouth. | Smoking Use of tobacco. |
Diagnosing mouth sores
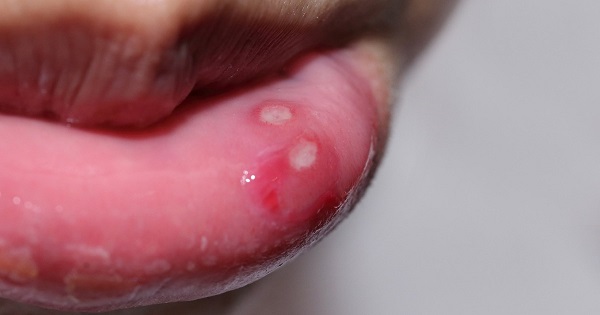
The most common reasons
Funnily enough, the most common non-medical reason for a mouth sore is your brush! Yes, your toothbrush. A hard toothbrush can damage the delicate lining of your mouth.
The next most common reason is accidentally biting the inner lining of your cheeks. Drinking or eating excessively hot food can also temporarily damage your oral cavity.
But these are simple, relatively harmless sores that will heal on their own.
Diagnosing the serious symptoms
Mouth sores are a serious cause for concern for any of the 3 reasons:
- If they do not heal on their own or heal with simple medication
- If they are recurrent.
- If they are accompanied by other symptoms.
Mouth sores require immediate medical diagnosis for the following reasons:
- Sores that appear after taking new medication.
- If you are a smoker and if you start getting mouth sores.
- If the mouth sore gets worse by time.
- Persistent symptoms of fever, loss of taste and appetite, increased pain around the site of the sore.
Diagnosis will usually include a thorough examination by a doctor with medical tests to rule out complications. Sometimes a biopsy will also be necessary, depending on the condition of the mouth sore and the other symptoms.
Prevention and Treatment of Mouth Sores
Get them treated
Like we discussed earlier, some mouth sores heal on their own within a few days. Some may require pain-relieving medication, anti-inflammatory drugs and steroid gels.
For more harmful viral infections of the oral cavity, doctors may prescribe a specific course of treatment depending on the seriousness of the issue. Oral cancers may require biopsies, chemotherapy and surgeries.

All you can do to prevent mouth sores
Mouth sores are common and cannot be forestalled once and for all. However, there are simple ways to prevent them from occurring.
- Use a soft toothbrush and take care not to harm the oral cavity while brushing.
- Chew and eat your food slowly to avoid biting the lining of your cheeks.
- Avoid extremely hot foods.
- Gargle regularly with salt water.
- Completely avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake.
- Use a mild lip-balm to keep them moist and prevent them from cracking.
- Keep yourself hydrated with plenty of water, tender coconut and fresh fruit juices.
- Increase your intake of foods rich in vitamin B.
Mouth sores are mostly harmless. But it is always wise to consult a doctor if symptoms persist.