Medical wastes: Effective hospital waste management process

Know about different kinds of medical equipment for doctors and nurses
February 28, 2020
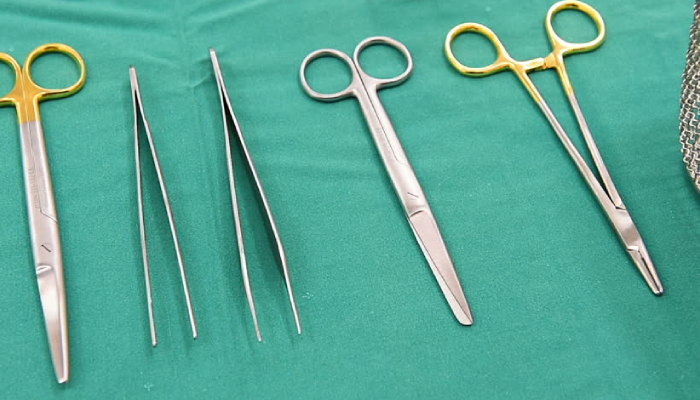
An overview of different medical tools for surgery
March 6, 2020Medical wastes are the wastes generated in the health care sectors that involve surgeries, hospitals, or laboratories. Any materials that are exposed to the body or bodily fluids during the treatment, diagnosis, research, or drug administration are put into the category of medical wastes. Hence, these wastes must be responsibly disposed of. Though the hospitals are committed to categories wastes and dispose of that correctly, the recent COVID 19 outbreak is emphasizing the need to be extra cautious in this matter. This article will take you through the different types of medical waste and the hospital waste management process implemented by the health sectors.
What are medical wastes and their different categories?
Medical wastes are the byproducts of different processes conducted at hospitals, pathological laboratories, nursing homes, blood banks etc. The debris also involves the ones generated during the medical camps held for immunizing humans and animals. Medical wastes can be typically infectious and have potential risks of spreading diseases. Hence, disposing of these wastes responsibly is of utmost necessity. Different countries have classified medical wastes into multiple categories that undergo different hospital waste management processes. In India and other significant parts of the world, the medical wastes are classified into four major categories: General, Infectious, Hazardous, and Radioactive.
Read More About : An Overview Of Different Medical Tools For Surgery
Classification of medical wastes
Though different countries name and classify the medical wastes differently, the most common classification is as follows
Infectious wastes
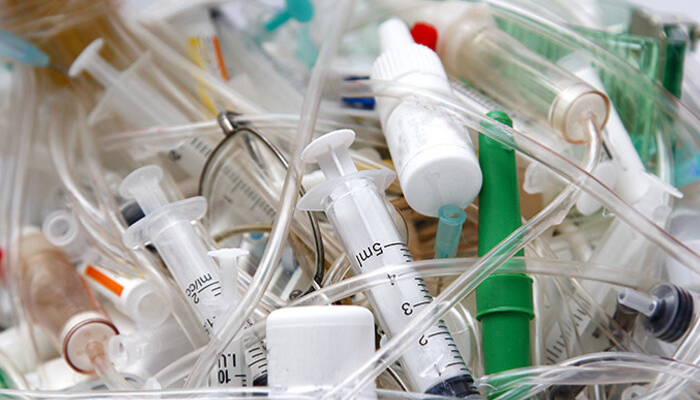
Blood, human tissues or any disposables like blood-soaked bandages, cultures, discarded gloves or swabs used for inoculating cultures are the contagious wastes. They have the potential of spreading infections. Several countries, including WHO classify the wastes like human or animal tissues as pathological wastes, which need a specific disposable method. These wastes are suspected of carrying pathogens.
It is also important to note that the instrument or tools that handle infectious wastes also belong to the infectious wastes categories. This may include syringes, scissors, gloves, scalpels, and other disposables.
Waste management process of infectious wastes
Autoclaving methods are used to inactivate infectious waste initially. This process is a sterilization process in which the infected instruments are sterilized with steam. The waste will be disposed of into red biohazard bags that are transferred to facilities for disposal.
The pathological waste that may include tissues, organs or other body parts contains high moisture contents, which requires it to be incinerated. The incineration process is the burning of the wastes and producing ash. The ash produced is packed and disposed of in a landfill.

Hazardous wastes
Sharp instruments discarded after surgical procedures or the chemical residues constitute the hazardous wastes. The hazardous wastes like syringes and instruments are generally non- infectious, but depending upon the origin as well as the exposure to animals or humans, it can be classified into infectious waste accordingly. In that case, those wastes need to clear all the waste management processes for contagious diseases as well. Sharp objects are potentially hazardous as they can lacerate or puncture the skin. Chemical wastes include old drugs and chemotherapy agents.
The waste management process for hazardous wastes
The healthcare facilities like hospitals and clinics generally have a designated area for the storage of hazardous wastes. Waste management contractors who are engaged by medical facilities take way these wastes periodically for treatment and disposal.
Radioactive wastes
Wastes generated from radioactive treatments like chemotherapies and equipment that use nuclear elements consists of radioactive wastes. The pathological wastes contaminated by radioactive elements are also considered as radioactive wastes.
The waste management process for radioactive wastes
Radioactive wastes decay over a specified period. Hence, the healthcare facilities usually store it on-site away from any human or animal exposure until its decay. The storage for radioactive wastes is done batch-wise. The best treatment method for these wastes is immobilizing radioactive waste and disposing of it off once the radio activeness has subsided.
General wastes
About 85% of wastes are general wastes that are no different from the household wastes. They are referred to as the municipal solid wastes and are disposed of in landfills.
It is essential to understand the different classifications of medical wastes for a proper waste management process and to protect the healthcare and sanitation workers from their harmful effects.